
Inicio / Doxepin
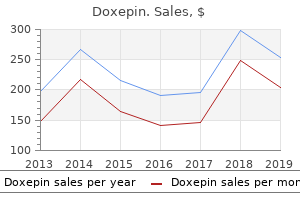
"Buy discount doxepin 10mg on line, anxiety symptoms diarrhea".
By: L. Ressel, M.A., M.D.
Clinical Director, Alpert Medical School at Brown University
Follicles-Follicles are seen in the upper and lower fornix anxiety 2 days after drinking purchase doxepin 75 mg on-line, palpebral conjunctiva anxiety 6 weeks pregnant purchase doxepin without prescription, plica anxiety attack symptoms yahoo answers purchase 75 mg doxepin visa, bulbar conjunctiva (pathognomonic) anxiety yelling buy doxepin online pills. Typical star-shaped scarring is seen at the centre of the follicles in late stages. Pannus-There is lymphoid infiltration with vascularization seen in the upper part of cornea. Progressive pannus-Superficial blood vessels are parallel and directed downwards. They extend to a horizontal level beyond which zone of infiltration and haze is present. Regressive pannus-The area of infiltration stops short and the blood vessels extend beyond this haze. Mac Callan Classification There are four clinical stages according to Mac Callan classification. Trachoma I (subclinical stage) It is the earliest stage before clinical diagnosis is possible. There is marked inflammatory thickening of the upper tarsal conjunctiva which appears red, rough, thickened with numerous follicles. Evidence of recent removal of inturned eyelashes should be regarded as trichiasis. Trichiasis and corneal ulcer Sequelae and Complications the only complication of trachoma is corneal ulcer. Xerosis-Scarring of conjunctiva results in destruction of goblet cells which secrete mucus. Medical Trachoma organisms are sensitive to tetracycline, sulphonamides, erythromycin, rifampicin, ciprofloxacin, azithromycine and sparfloxacine is also effective in trachoma. Elinimation of secondary infection of conjunctiva is done by antibiotic eyedrops. Topical treatment with 1% erythromycin, 1% tetracycline or rifampicin ointment is far more effective. Systemic administration of tetracycline, erythromycin, rifampicin and sulphonamides is effective. Sulphonamides can cause allergic reaction like Stevens-Johnson syndrome, skin rash. Tetracycline cannot be given to young children, pregnant women and nursing mothers as it adversely affects the enamel formation of the teeth. Nowadays treatment with a single dose of azithromycin 2 mg/kg body weight has been recommended. Combined topical and systemic treatment It is preferred when the ocular infection is severe. Excision of fornix-If the follicles in the upper fornix are very large and closely packed, excision of the fornix can be done. Tarsectomy-If the tarsal plate is much diseased and distorted, tarsectomy may rarely be performed. Treatment of various sequelae such as trichiasis, entropion, dry eye should be done. The regime is to apply 1% tetracycline eye ointment twice daily for 5 days per month. Acute or Subacute Catarrhal Conjunctivitis Etiology It is an acute or subacute non-specific urticarial reaction to allergen. Staphylococcus in nose or upper respiratory tract can cause this condition commonly. Exogenous protein as in hay fever, contact with animals (horse, cat), pollens or flowers. Differential Diagnosis It can be differentiated from acute bacterial infection by the following features: i. Antihistamine drugs (antistine privine1%) are effective in controlling allergic reaction. Disodium cromoglycate 2% is a mast cell stabilizer, thus, preventing the release of histamine. Phlyctenular Conjunctivitis (Eczematous Conjunctivitis) It is an allergic reaction of the conjunctiva caused by endogenous protein characterised by formation of bleb or nodule near the limbus (phlycten = bleb). It is caused by allergic reaction to endogenous bacterial protein such as tuberculosis.
As in Salter 3 fractures anxiety help discount doxepin 75 mg line, the physis is injured and the fracture is intra-articular anxiety buzzfeed order doxepin 25mg otc. It is more likely that the initial diagnosis of a nondisplaced Salter 1 fracture will be made anxiety numbness buy 75mg doxepin otc, and only with growth complication will the true nature of the injury reveal itself anxiety episode order doxepin pills in toronto. Salter 6 - this classification was coined by Rang and describes an injury to the perichondral ring surrounding the physis (direct blow, burn, local infection). Although the physis is uninjured, the inflammatory process may lead to bone formation, bridging the epiphyseal-metaphyseal junction, effectively tethering growth at the physis and resulting in a progressive growth deformity. Parents should always be educated and informed from the onset that a physeal injury may lead to a growth aberration later. Greenstick fractures - occur when stress is applied to a long bone such that the cortical bone fails in tension but not in compression. The "intact" cortex typically undergoes compression and plastic deformity due to radiographically invisible microfracture. Plastic deformity may hinder the ability to adequately correct angulation and hold the reduction at the fracture site (hence, the practice of "completing" the fracture prior to reduction and immobilization). These bumps result when an axial compressive load causes microfracture and localized plastic deformity rather than a radiographically apparent cortical break. Fractures of the hand are relatively uncommon (5-7% of fractures) and only 1/3 involve a physeal injury. Rapid healing is the rule, so prompt orthopedic referral is necessary (healing in malposition may make a minor injury more problematic). Pediatric Mallet Equivalent Top is a displaced Salter 1 injury of the distal phalanx, typical of the preadolescent. In the adolescent (with partial fusing of the epiphysis), a Salter 3 injury of the distal phalanx may occur with the same mechanism. Open fractures are cleaned and irrigated with minimal Pediatric Orthopedics Page 323 Notes debridement. Partial tip amputations are reapproximated and do remarkably well with even minimal remaining pedicle. Middle and proximal phalangeal fractures are most commonly Salter 1 or Salter 2 with the ring and small digit most commonly involved. Rotational deformities are best appreciated by examining the attitude of the nail beds with the phalangeal joints in flexion. Scaphoid fractures are not seen until 10 to 12 years of age, and as with adults, a high level of suspicion is required. Emergency management includes immobilization in a thumb spica splint with prompt follow-up. The mechanism is typically a fall on an outstretched hand with a hyperextended wrist. The most common pediatric orthopedic injury is the Salter 2 fracture of the distal radius. Distal radius fractures are typically Salter 1 or 2 physeal injuries, torus or Greenstick fractures of the distal metaphysis, or complete fracture (both radius and ulna). Complete fractures typically have the "dinner fork" deformity similar to adult Colles fractures. Occult wrist fractures may cause anterior displacement of the normal pronator quadratus fat pad seen on the lateral view along the volar aspect of the radial metaphysis. Always X-ray the entire forearm when a distal fracture is found, to rule out proximal injury. Emergency department reduction is indicated for severe deformity with tenting or compromise of overlying skin, or neurovascular compromise. Lesser degrees of deformity can be treated with immobilization and prompt referral. Pediatric Orthopedics Page 324 Notes Remember, in any physeal injury, multiple reduction attempts are not advised - each manipulation can further injure the physis. As in distal fractures, they are described as Greenstick, torus, or complete fractures, and further defined by the level (proximal third or middle third). As in adults, an obvious fracture of the ulna should prompt evaluation for radial head displacement (Monteggia fracture). Complete fracture in this area is particularly prone to refracture in the first six months.
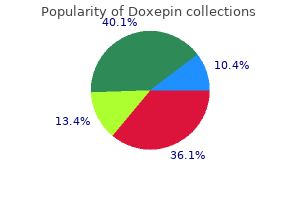
Order doxepin 10mg with mastercard. Healing Narcissistic Abuse Anxiety Depression--Tips On Controlling the Mind.

Slit-lamp examination shows irregular margins of the ulcer and details of anterior segment of the eye anxiety symptoms in cats purchase cheap doxepin online. It is so very faint that the finer details of iris are clearly visible through the opacity anxiety symptoms associated with ptsd purchase on line doxepin. A thin diffuse nebula covering the pupillary area interferes more with vision than localized dense leucoma not covering the whole pupillary area anxiety 100 symptoms generic doxepin 75mg overnight delivery. Optical effect of nebula · irregular astigmatism Optical effects of Leucoma · stops all light which falls upon it · loss of brightness but not definition 2 anxiety buzzfeed buy discount doxepin 25 mg line. Macula-The corneal opacity is dense when it involves about half the thickness of the stroma. Leucoma-A thick white, dense and totally opaque scar results when almost full thickness of stroma is involved. Ectatic Cicatrix [Keratectasia] (ectasia = bulge forwards, cicatrix = fibrous scar) There is marked thinning at the site of ulcer. Descemetocele [Keratocele] Few ulcers specially those due to pneumococcus and septic organisms extend rapidly. Perforation Etiology-Sudden strain due to cough, sneez or spasm of orbicularis muscle may cause perforation. The only benefit is that the nutrition of the cornea improves, pain is relieved and scarring takes place. Prolapse of iris-When part of iris protrudes through the ulcer it is known as prolapse of iris. Anterior synechia-The adhesion of iris to the posterior surface of cornea is known as the anterior synechia. Adherent leucoma-It is a leucomatous opacity in which the iris tissue is incarcerated within the layers of the cornea. Anterior staphyloma-The adherent leucoma becomes ectatic due to secondary glaucoma or weakness of corneal scar tissue. The opening in the cornea is lined by the epithelium therefore it does not heal leading to fistula formation. Anterior capsular cataract-It is formed when the lens comes in contact with the ulcer. Dislocation or subluxation of lens occurs due to stretching and rupture of zonule. Intraocular haemorrhage-Sudden lowering of intraocular pressure results in dilatation and rupture of choroidal blood vessels leading to intraocular haemorrhage. Purulent iridocyclitis and panophthalmitis usually occurs in gonococcal infection and hypopyon ulcers. Control of infection Infection is controlled by intensive local use of antibiotic drops. It paralyses the ciliary muscles and provides comfort to the eye by preventing ciliary spasm. There is associated iritis always in cases of corneal ulcer due to penetration of endotoxin across the endothelium in the anterior chamber. Same as adherent leucoma Dense, white opacity of cornea Etiology · Perforated · Healed corneal ulcer corneal ulcer · Iridocyclitis · Healed keratitis · Closed angle · Penetrating glaucoma injury · Foreign body · Corneal dystrophy · Perforated corneal ulcer · Penetrating injury · Operating wound Anterior synechia Symptoms 1. Visual acuity Normal Leucoma Impaired if situated over pupillary area Flat Fine yellowish brown lines in the epithelium (Hudson Stahlis) haemosiderin, melanin Normal Adherent leucoma Anterior staphyloma Impaired if situated over pupillary area Flat Brown pigment from iris are present Impaired Signs 1. Intraocular tension Normal or shallow Normal Normal Normal or raised when more than 3/4 circumference is involved (closed angle glaucoma) Normal Impaired over opacity Normal Irregular or shallow where iris comes forwards Drawn towards adhesion Impaired over opacity Normal or raised (secondary glaucoma) Usually absent or very shallow Not seen Impaired Raised usually the Cornea 115 ii. A shield or dark glasses are used if there is associated conjunctival discharge to avoid retention of secretion, which in turn favours bacterial growth due to warmth and stasis. Procedure Bacterial corneal ulcer is a serious condition that requires immediate treatment by identification and eradication of causative organism. Causative organism can be identified by smear preparation, culture and sensitivity test of the scrapings taken from the base of the ulcer.
There are serpiginous areas of anechoic echogenicity associated with the renal medulla with cortical extension in keeping with moderate pelivocalyceal dilatation (Figure 71 anxiety eating disorder buy doxepin on line amex. The patient ultimately requires a definitive surgical procedure to remove the cancer anxiety problems order doxepin 75 mg mastercard, but at present anxiety symptoms stomach pain buy doxepin us, the ureteric obstruction and deterioration in renal function makes the patient biochemically unstable anxiety while sleeping cheap 75 mg doxepin with mastercard. Surgery carries significant risk, and in a non-life threatening situation, the patient should be physically and biochemically optimized to encourage a safe transition through the operation, reduce the risk of intra-operative mortality and improve post-operative recovery. Cystoscopy can be performed under conscious sedation but general anaesthesia is preferred. The patient lies on a fluoroscopy table in the prone position, and a micropuncture needle is passed percutaneously under direct ultrasound imaging into a dilated lower pole calyx. Instilling contrast into the collecting system under fluoroscopy can confirm satisfactory positioning (Figure 71. Adopting the Seldinger technique, a guidewire can then be manipulated into the proximal ureter over which a sheath is passed to stabilize the position. This allows careful manipulation of an appropriately sized renal stent to be passed over the wire so that one end lies within the bladder, and the other lies more proximally within the renal pelvis. This acts as a conduit through which urine can drain for renal decompression (Figure 71. Stent positioning requires a high level of accuracy and it may also become obstructed both by tumour overgrowth and stent migration. As a precautionary measure, an additional pigtail catheter is often left within the renal pelvis, running along the line of the original percutaneous puncture to act as a urinary diversion both for initial decompression and in case of stent failure. This is termed a covering nephrostomy and remains in position for the short term (Figure 71. Renal decompression will allow time for the renal function to return to normal and means that the operation can be performed in a less urgent and more controlled environment. Holistically, it also allows for the patient to make appropriate decisions about their own management. The nephrostomy and stent can be removed intra-operatively, leaving only a small cutaneous scar. She is immobilized on a board with a hard neck collar and complains of diffuse neck pain and mild intermittent tingling in the arms and legs. There is no history of loss of consciousness, no evidence of head injury (she had a riding helmet on) and no complaint of injury elsewhere. There is no significant past medical history although the patient has had intermittent neck pain in the past that has not been investigated. Examination Routine observations are stable and she is maintaining her airway, breathing and circulation. You perform a primary survey which reveals diffuse tenderness in the mid cervical spine. There is overlying artefact as the images are obtained with immobilization blocks. When assessing cervical spine radiographs, there are a number of lines that should be viewed to help pick up abnormalities. On the lateral projection, the anterior and posterior vertebral edges describe lines. The line through the junction of the lamina and the anterior edge of the spinous processes (spinolaminar line) and the curve through the posterior tips of the spinous processes should be reviewed. These lines should all be smooth and continuous with no steps, although the natural curvature of the neck may be altered due to pain or immobilization. Any small fragments of bone should be considered for fractures although may be ossification centres in younger patients or degenerative changes in older patients. No fracture is identified, however, the appearance suggests a chronic expansile bone lesion involving the pedicles and spinous process of C5 that may be narrowing the spinal canal. No significant soft tissue swelling or periosteal reaction is seen to suggest an aggressive process. Spinal stenosis can be congenital or acquired and most often affects the cervical or lumbar spine. Degenerative change or metastatic bone lesions are common causes in patients over 50.
Si quieres mantenerte informado de todos nuestros servicios, puedes comunicarte con nosotros y recibirás información actualizada a tu correo electrónico.

Cualquier uso de este sitio constituye su acuerdo con los términos y condiciones y política de privacidad para los que hay enlaces abajo.
Copyright 2019 • E.S.E Hospital Regional Norte • Todos los Derechos Reservados
